Is your rotavirus vaccine indicated to help prevent RGE caused by G2?1
RotaTeq is the only rotavirus vaccine indicated to help protect against RGE caused by 5 strains, including G21


RotaTeq is indicated for the prevention of rotavirus gastroenteritis in infants and children caused by Types G1, G2, G3, G4, and G9 when administered as a 3-dose series to infants between the ages of 6 to 32 weeks. The first dose of RotaTeq should be administered between 6 and 12 weeks of age.


Rotarix is indicated for the prevention of rotavirus gastroenteritis caused by G1 and non-G1 types (G3, G4, and G9) when administered as a 2-dose series. Rotarix is approved for use in infants 6 weeks and up to 24 weeks of age.1
G2 type – genetically distinct from other common rotavirus types.2,3
These 5 common rotavirus strains belong to 2 distinct, minimally related genogroups.
Wa GENOGROUP
G1P[8] , G3P[8] ,G4P[8], G9[8]


DS-1 GENOGROUP
G2P[4]
- Of the common types, G1, G3, G4, and G9 are typically associated with protein P[8], while G2 is commonly associated with protein P[4].2,3
- In other words, G2 strains generally do not share P surface proteins with the other most common rotavirus G types.2,3
8-year active CDC surveillance study showed rotavirus strains varied from season to season, with G2 present in every year:4
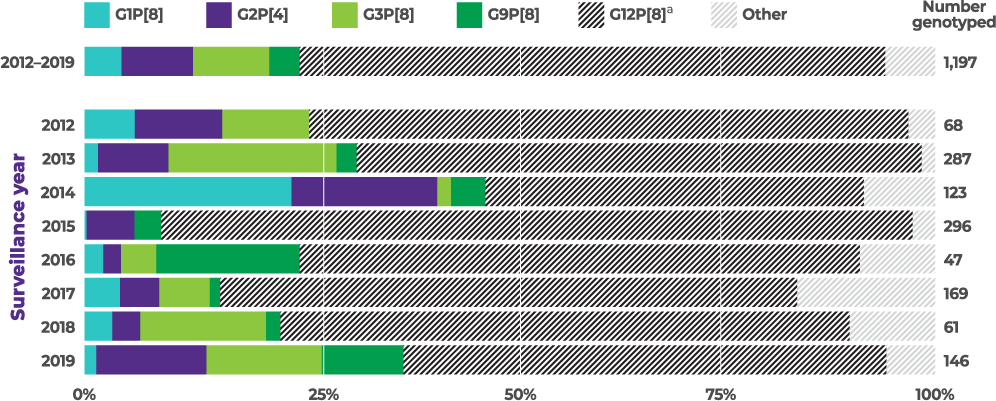
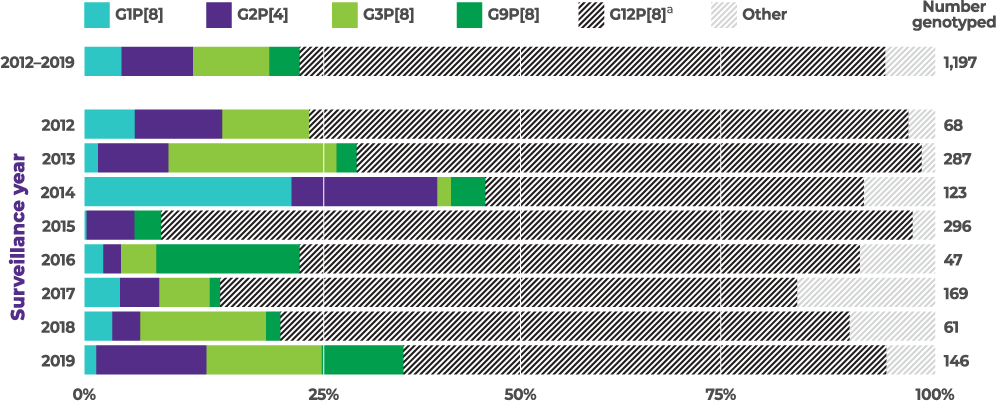
Distribution of common genotypes detected among children aged 8 to 59 months by surveillance year, NVSN, 2012 to 2019 (N=1,197)
aNone of the current rotavirus vaccines are indicated to cover strain G12.1
Study design:
The CDC used a test-negative, case-control design to estimate rotavirus VE against laboratory-confirmed rotavirus infections among children aged 8 months and older (N=16,188) who visited the ED or were admitted to the hospital at 8 US NVSN sites from 2009–2022 (equivalent to calendar year end 2010 to 2022). Across the 13 surveillance years, the study examined rotavirus case prevalence, vaccine coverage, and calculated VE at preventing rotavirus-associated ED visits or hospitalizations. All analyses were restricted to children 8 months to 4 years, except for the age-stratified VE estimates, which included children 8 months to 17 years. Rotavirus genotype data from 2012–2019 were analyzed for children 8 months to 59 months (N=1,197).4
CDC, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; ED, emergency department; NVSN, New Vaccine Surveillance Network; RGE, rotavirus gastroenteritis; VE, vaccine effectiveness.
From 2012–2019, G2 was the second most commonly reported of 4 vaccine-covered strains (G1, G2, G3, and G9)1,4,a,b
Among vaccine-covered strainsa (n=303/N=1,197, 25.3% of all reprted strains) in specific patient populations1,2
G2 was the most common strain in4,c:


G2 was the second most common strain in4,c:


aVaccine-covered strains include G1, G2, G3, and G9. Prevalence of G4, a vaccine-covered strain, was not specified. None of the current rotavirus vaccines are indicated to cover strain G12.1,4
bBetween 2012–2019 and among vaccine-covered strains (N=303), 35.3% (N=107) of cases were attributed to G3, 32.7% (N=99) were attributed to G2, 17.2% (N=52) were attributed to G1, and 14.9% (N=45) were attributed to G9 in children <5 years of age.1,4
cThe prevalence of G2 among vaccine-covered strains (G1, G2, G3, G9) was calculated by dividing the number of G2 cases in specific populations (n) by the total cases for vaccine-covered strains in that population (N).1,4


Looking to stock RotaTeq in your practice?
Simply register or log in to your account to get started.

CDC recommendations
Find out about the CDC recommendations for rotavirus vaccination in pediatric patients.5

Dosing and administration
Review the dosing schedule and administration of RotaTeq.
References
- Rotarix. Prescribing information. GSK; 2024.
- Dennis AF, McDonald SM, Payne DC, et al. Molecular epidemiology of contemporary G2P[4] human rotaviruses cocirculating in a single U.S. community: Footprints of a globally transitioning genotype. J Virol. 2014;88(7):3789-3801.
- Matthijnssens J, Van Ranst M. Genotype constellation and evolution of group A rotaviruses infecting humans. Curr Opin Virol. 2012;2(4):426-433.
- Diallo AO, Wikswo ME, Sulemana I, et al. Rotavirus vaccine effectiveness against severe acute gastroenteritis: 2009–2022. Pediatrics. 2024;154(4):e2024066879. doi:10.1542/peds.2024-066879
- Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). Recommended child and adolescent immunization schedule for ages 18 years or younger, United States, 2025. Last reviewed October 7, 2025. Accessed October 27, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/hcp/imz-schedules/downloads/child/0-18yrs-child-combined-schedule.pdf
