
ACIP recommends rotavirus vaccination to help protect infants1
ACIP recommendation for rotavirus vaccination1
The ACIP recommends routine vaccination of US infants at least 6 weeks of age with a rotavirus vaccine.1
In addition to the ACIP, the AAFP and AAP recommend routine rotavirus vaccination for all eligible infants in order to protect infants against rotavirus and reduce rotavirus morbidity.1-3
Can be completed as early as 14 weeks of age (doses given at 6, 10, and 14 weeks of age). Third dose should not be given after 32 weeks of age. The safety and efficacy of RotaTeq have not been established in infants less than 6 weeks of age or greater than 32 weeks of age.
AAFP, American Academy of Family Physicians; AAP, American Academy of Pediatrics; ACIP, Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices; CDC, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Despite vaccination rates of approximately 75%, there’s still more to do4
children in the US has not been vaccinated against rotavirus.
National Immunization Survey-Child, United States, 2017-2021. Children born during 2018 and 2019 (N=29,598).
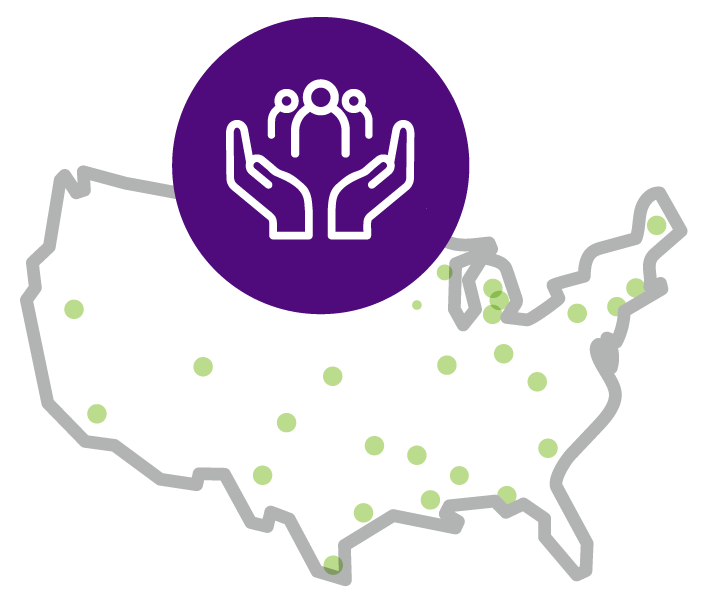
Help protect your patients by vaccinating them5
Despite good rotavirus vaccination rates in the US, geographic hotspots have been reported with vaccination rates below the national average and rates of rotavirus-related medical encounters above the national average. US counties mapped in green had both low vaccination rates and high rotavirus-related visit rates in a single month between 2015-2017.5,a
aIn 2015-2017, the national rotavirus vaccination rate, calculated using 1996-2017 data from a large US national insurance claims database, was 70%. Rotavirus-related hospital visit rates in counties with vaccination rates less than 70% were 5 times higher than the national average (1 per 1,000 eligible population).5
RGE, rotavirus gastroenteritis.
Helpful information for parents
Parents may feel overwhelmed with the number of vaccines their baby will receive in the first few months. Here is a useful link that you can give them that may help.
Vaccines for Children (VFC) Program
RotaTeq is well established in the VFC Program. Sign up to participate and help provide all routine vaccinations recommended by the CDC’s ACIP to your eligible patients.6

Dosing and administration
Review the dosing schedule and administration of RotaTeq.

Rotavirus strain coverage
Learn why broad coverage matters and how RotaTeq helps protect against RGE caused by various strains of rotavirus.7
References
- Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). Recommended child and adolescent immunization schedule for ages 18 years or younger, United States, 2024. Accessed May 29, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/schedules/downloads/child/0-18yrs-child-combined-schedule.pdf
- Committee on Infectious Diseases; American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP). Prevention of rotavirus disease: updated guidelines for use of rotavirus vaccine. Pediatrics. 2009;123(5):1412-1420. doi:10.1542/peds.2009-0466
- Cortese MM, Parashar UD; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Prevention of rotavirus gastroenteritis among infants and children: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR Recomm Rep. 2009;58(RR-2):1-25.
- Hill HA, Chen M, Elam-Evans L, Yankey D, Singleton J. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Vaccination Coverage by Age 24 Months Among Children Born During 2018–2019 — National Immunization Survey–Child, United States, 2019–2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72:33–38. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/72/wr/mm7202a3.htm
- Mast CT, Heyman D, Dasbach E, et al. Planning for the introduction and effectiveness of new vaccines using real-world data and geospatial visualization: an example using rotavirus vaccines with potential application to SARS-CoV-2. Vaccine X. 2021;(7);100084. doi:10.1016/j.jvacx.2021.100084
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Vaccines For Children (VFC) Program Information for Providers. Last Reviewed March 4, 2024. Accessed May 29, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/programs/vfc/providers/index.html
- Staat MA, Payne DC, Halasa N, et al. Continued evidence of the impact of rotavirus vaccine in children less than 3 years of age from the United States New Vaccine Surveillance Network: a multisite active surveillance program, 2006-2016. Clin Infect Dis. 2020;71(9):e421-e429. doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa150
